Phone:
+86 13828 600940
Physical address:
No.8Liyuan Road, Bogang community, Shajing Street Baoan District, Shenzhen, China
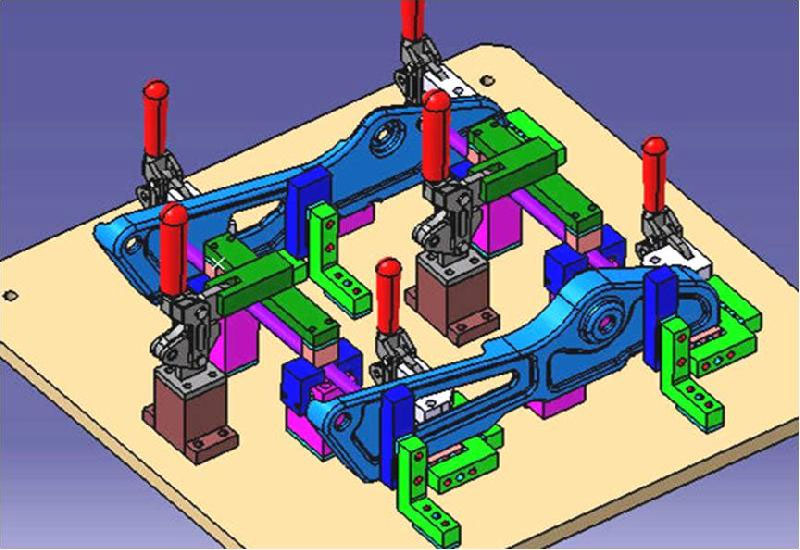
Fixture design is the process of determining the specific requirements of a part’s machining process, performed according to the specific requirements of one or all processes. Fixture design should consider the feasibility, safety, cost-effectiveness, ease of operation, and sustainable maintainability of the part’s machining process. The quality of the fixture design directly affects the quality and efficiency of part machining.

The structure of universal fixture has been standardized, and there are fixtures with a wide range of applications, such as three-jaw chucks and four-jaw chucks, flat-nose pliers and indexing heads.




Special machine tool or robot fixtures are specially designed and manufactured for a specific process of a workpiece. They are suitable for applications where the product is relatively stable and the output is high.
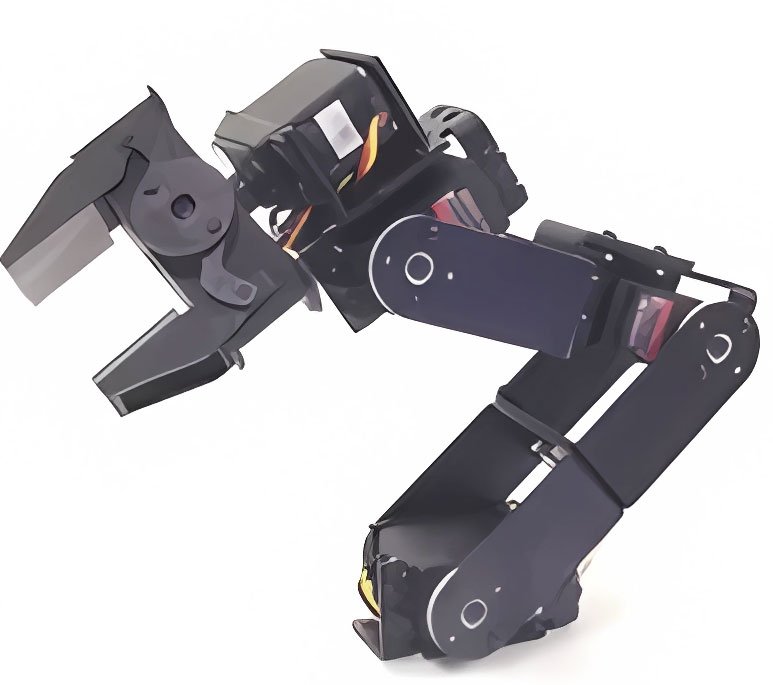
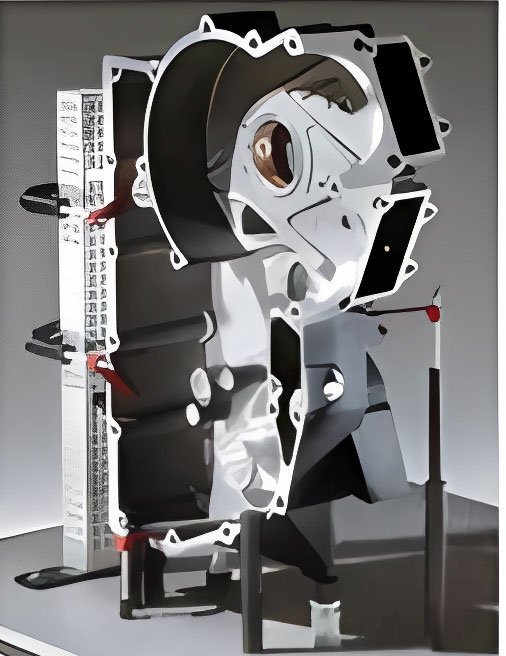



A modular fixture is assembled from standard components and assembly parts. This type of fixture is flexible and versatile, with a short design and assembly cycle and long-term reusability of parts. It is suitable for small-batch production of multiple products or trial production of new products.
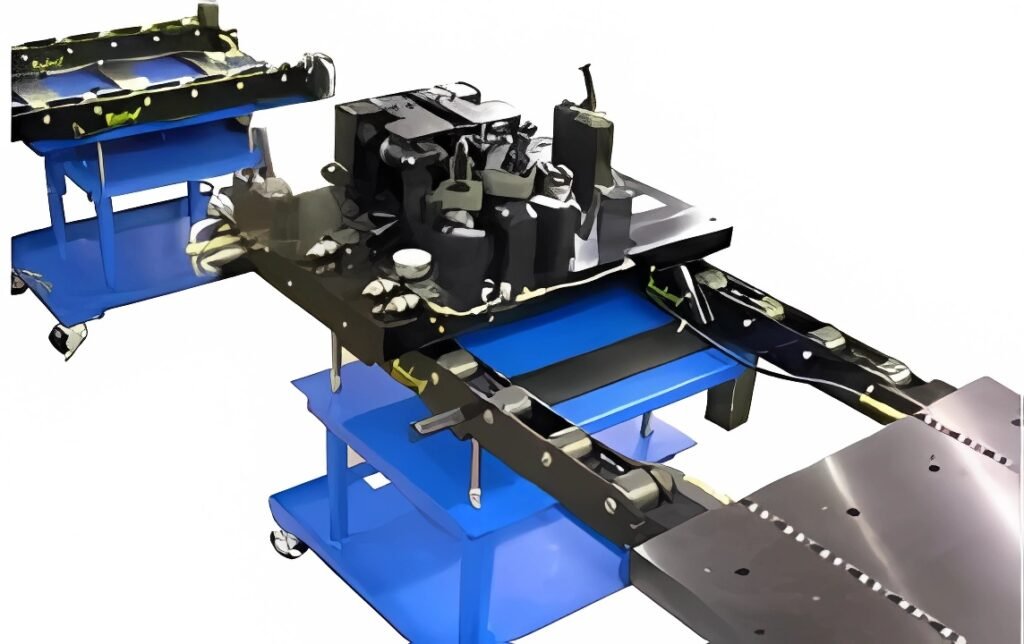
This is a mobile fixture used on automated production lines. Before a workpiece enters the automated production line, it is first placed in the fixture. The fixture and the workpiece are then moved from one station to the next along the automated production line. The workpiece is not removed from the fixture until it exits the automated production line. A travel fixture is a fixture that always moves along the automated production line with the workpiece.
A well-designed fixture must meet the following basic requirements:
The following original materials are required for the preparation before design:
a) Design notice, finished part drawing, rough drawing and process route and other technical information, understand the processing technology requirements of each process, positioning and clamping scheme, the processing content of the previous process, the rough condition, the machine tools, cutting tools, inspection tools used in processing, processing allowance and cutting amount, etc.;
b) Understand the production batch and the demand for fixtures;
c) Understand the main technical parameters, performance, specifications, accuracy of the machine tool used, and the dimensions of the connection part with the fixture;
d) Inventory status of standard materials for fixtures.
The fixture design must be systematically considered, otherwise unexpected troubles may occur if you are not careful:
a) The rough allowance of the workpiece. This can cause the rough size to be too large, resulting in interference. Therefore, a rough drawing must be prepared before designing. Leave enough space.
b) Ensure smooth chip removal in the fixture. Due to the limited processing space of machine tools, fixtures are often designed to be compact. This often leads to the accumulation of chips in the fixture’s dead corners, which can lead to poor chip removal and subsequent processing complications. Therefore, consideration should be given to potential issues arising from the machining process from the outset. After all, fixtures are designed to improve efficiency and facilitate operation.
c) The overall openness of the fixture. Ignoring the openness will make it difficult for the operator to install the fixture, which will be time-consuming and labor-intensive, and is a major design taboo.
d) Basic theoretical principles of fixture design. Every fixture undergoes countless clamping and loosening cycles, so while it may initially meet user requirements, the fixture must maintain its accuracy. Avoid designs that violate these principles. Even if it works temporarily, it won’t be sustainable in the long run. A good design should stand the test of time.
e) Replaceability of positioning components. Positioning components are subject to severe wear, so quick and easy replacement should be considered. It is best not to design them as large parts.