Phone:
+86 13828 600940
Physical address:
No.8Liyuan Road, Bogang community, Shajing Street Baoan District, Shenzhen, China
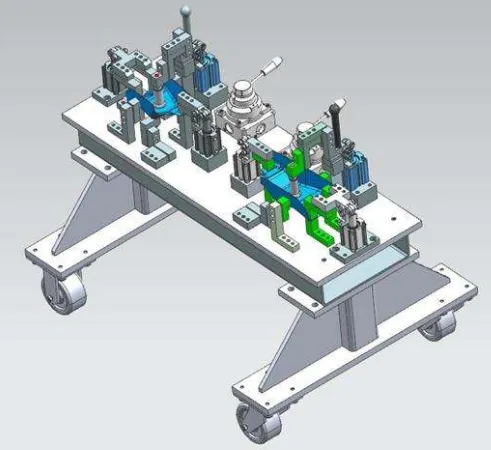
“Jiji” is a direct translation of the Japanese kanji. Due to Japan’s long-term rule in Taiwan, the term gradually became common in Taiwan. With the influx of Taiwanese businesses into China, the term “jig” has also spread throughout the country. Also called a jig in China, it typically refers to specialized tools used to secure (hold) products for processing (assembly) and quality testing during mass production.
Jigs are divided into two types: tooling jigs and inspection jigs. The former is a kind of tooling jig designed for machining, welding, assembly and other processes to facilitate processing and meet the needs of precision. The latter is used for testing. Because some products are difficult to measure in size and have complex shapes, we have to design special detection blocks or inspection tools for a certain product.
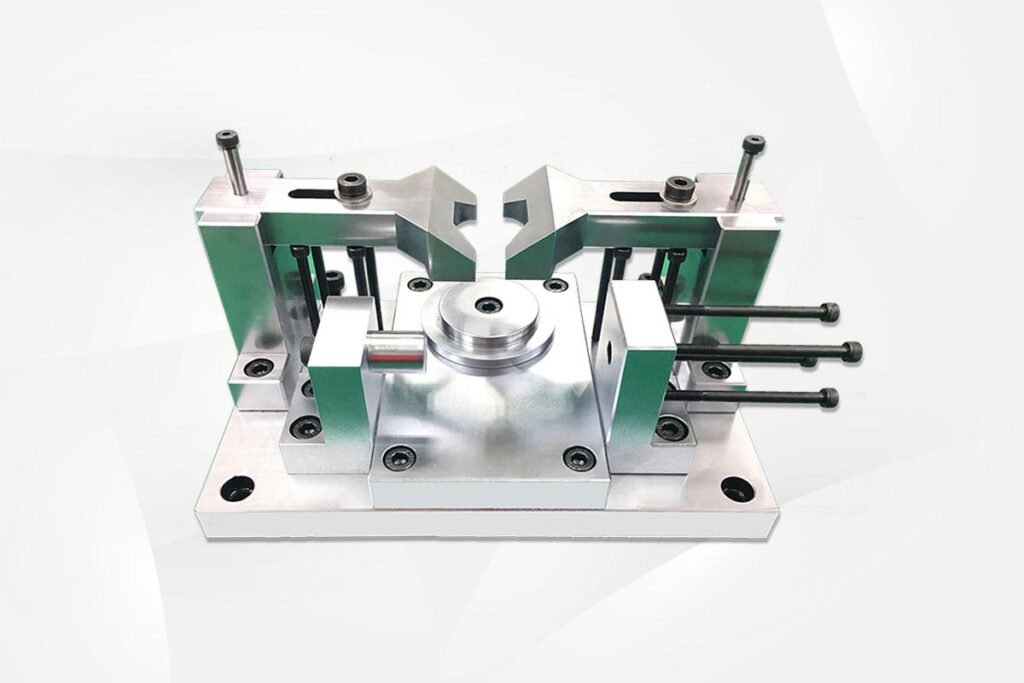
Welding jig: A special tool designed and manufactured for a certain welding product, used to fix (clamp) the product during the welding process for easy assembly.
Inspection jig: A specialized tool designed for a specific product to improve production efficiency and control product quality, used to inspect product dimensions. Due to the characteristics of welding structure and welding process, the positioning and clamping of welding workpieces on the jig are different from those used in machining. This gives welding jigs the following characteristics:
Since welding products are generally assembled and welded by multiple simple parts, and the assembly and positioning of these parts in the jig must be carried out in a certain order , the positioning and clamping of the jig must be carried out separately.
In order to reduce or eliminate welding deformation, the jig must rigidly position and clamp certain parts.
The welding jig for fusion welding is mainly subjected to welding stress, clamping reaction force and single-piece gravity during operation.
Some welding jigs are part of the secondary circuit of the welding power supply, so insulation and conductivity are an issue that must be paid attention to during design. For example, when designing welding jigs, such as insulation.
When selecting and designing welding jigs, the requirements for jigs vary due to differences in products and welding processes. However, most welding jigs have certain commonalities:
The jig should be quick and easy to operate. In particular, the operating position of the manual jig should be in a position that is most accessible and convenient for the operator. The operating force should not be too large and the operating action should be as few as possible.

The jig should have sufficient space for assembly and welding. It should not interfere with the operator’s operation and observation, nor hinder the loading and unloading of workpieces. All positioning and clamping mechanisms should maintain an appropriate distance from the weld bead, and some clamping and positioning devices must have telescopic and indexing functions.
The clamping must be self-locking, such as a cylinder or other device that can ensure that the clamping state does not change even in the event of a gas or power outage.
Reliable clamping. Clamping does not disrupt the workpiece’s positioning or geometry. It prevents loosening of the part and prevents excessive clamping force. While theoretically necessary for clamping, for some products, clamping is sufficient as long as it prevents displacement and deformation during welding.
Jig parts close to the welding area should be kept away from air and prevent damage from welding spatter.
Some parts of the jig must have a certain degree of rigidity to ensure low wear, such as positioning pins, positioning holes, support PINs, etc.
The positioning and clamping devices of the jig are easy to debug and replace
The parts on the jig should use common standard parts as much as possible
The main purpose of the jig is to quickly and accurately position the workpiece and maintain appropriate support so that all workpieces produced on the same jig are fixed within a specific range, ensuring the precision and interchangeability of the product.
Using jigs can reduce working time and perform work more efficiently in various processing, assembly and other tasks.
Complex work can be simplified, economic efficiency can be improved, and work that can only be completed by skilled workers can be completed by unskilled workers.
Simply put, it can improve productivity, ensure product quality and interchangeability, and reduce processing (assembly) costs.